Ethereum network gas fees fall to record low in November
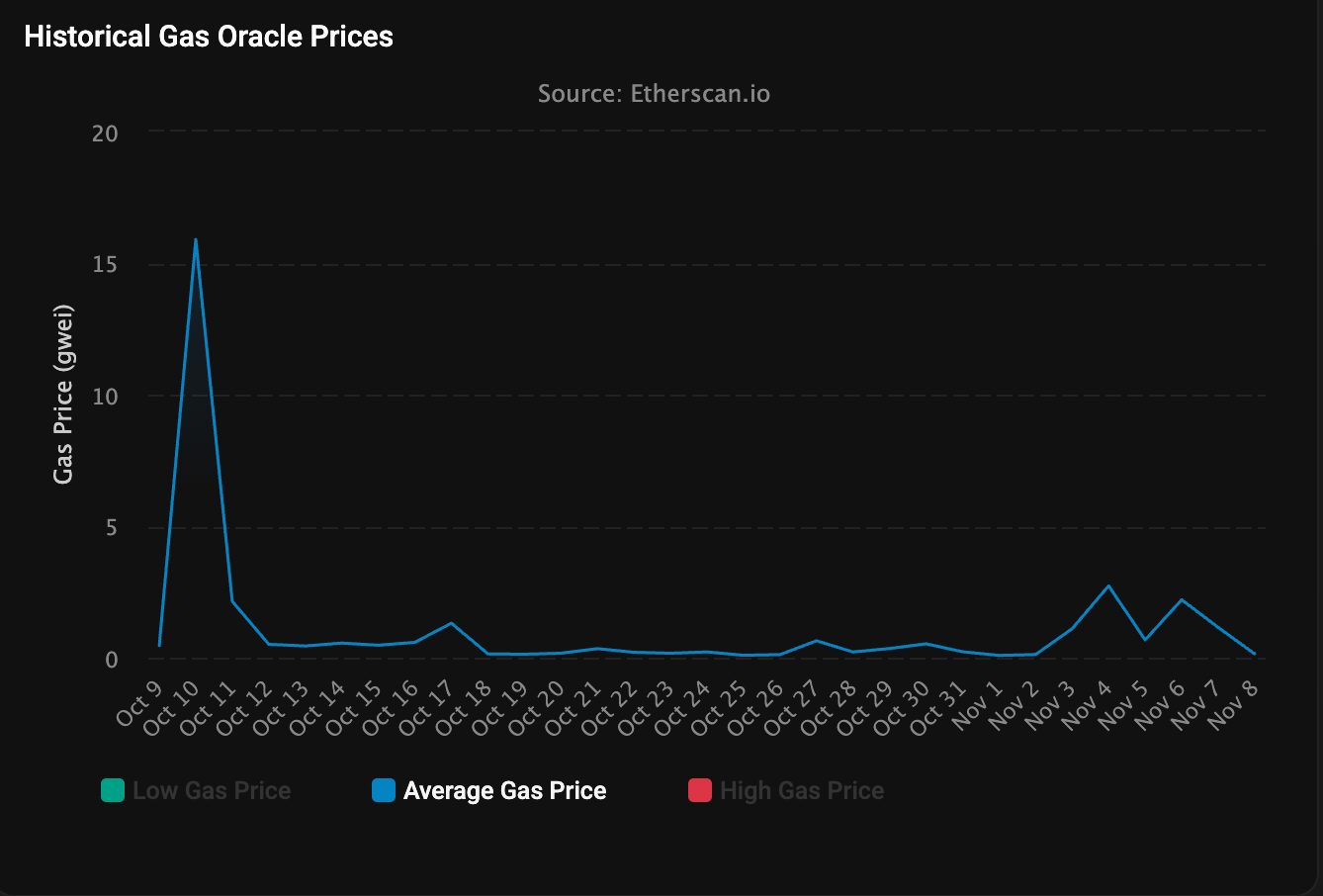
Ethereum network gas fees have dropped sharply, reaching just 0.067 gwei on Sunday, marking the lowest levels seen in 2024. The reduction follows a period of subdued activity in the crypto markets, triggered by October’s significant market crash.
Background: Understanding the Drop in Ethereum Network Gas Fees
The average cost to execute a swap on the Ethereum mainnet now stands at just $0.11, with non-fungible token (NFT) sales priced at $0.19, bridging assets at $0.04, and onchain borrowing at $0.09, according to Etherscan. By comparison, on October 10—at the height of the flash crash—transaction fees rose to 15.9 gwei as users rushed to make trades during high volatility. Just two days later, gas fees retreated dramatically, falling to 0.5 gwei and have since hovered below 1 gwei throughout October and November.
Market Reaction and Onchain Activity
With Ethereum network gas fees at historic lows, investors and traders currently have reduced costs to conduct onchain transactions. Some market participants may take advantage of cheaper fees for swaps, NFT trades, or inter-blockchain bridges. During the 2021 bull run, network congestion pushed Ethereum transaction fees to $150 or more. Today’s reduced fees provide an opportunity for more affordable blockchain use.
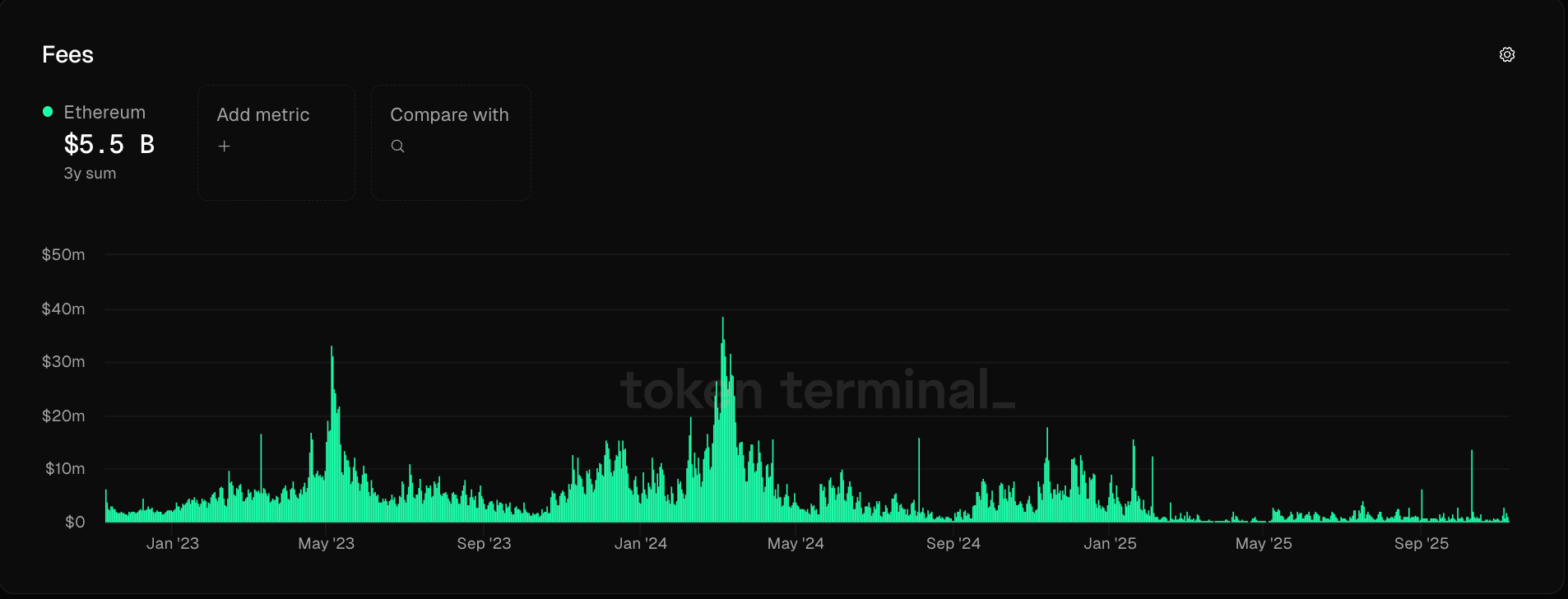
However, experts caution that the current situation could signal underlying problems. According to reporting by Cointelegraph, critics warn that persistently low transaction fees have significant implications for the Ethereum ecosystem’s economic health and security. Ethereum’s revenues have fallen by 99% since the March 2024 Dencun upgrade, which further slashed fees for layer-2 scaling networks.
Sustainability and the Future of Ethereum Fee Model
Low fees may undermine incentives for validators who process transactions and secure the blockchain, posing potential risks to network security. Blockchain revenue declines can also suggest that user demand is weakening or migrating to other networks. According to research by Binance cited in Cointelegraph, Ethereum’s scaling strategy, which depends on separate layer-2 networks, is creating internal competition for transaction revenue. While these layer-2 networks help Ethereum scale and remain competitive against new high-throughput blockchains, they may also erode the economic foundation of the Ethereum mainnet.
Industry observers are closely monitoring these developments to gauge their long-term effects on the ecosystem’s viability and the incentive structures for validators. The coming months will show whether lower Ethereum network gas fees will drive increased onchain activity, or if they point to more complex challenges for the platform in sustaining its security and market share.
For ongoing updates on Ethereum and blockchain trends, visit Vizi Cryptocurrency News.
Sources:
Cointelegraph



















