Uganda CBDC Pilot Launches Amid Kenya Crypto Law Progress
Background: Uganda CBDC Pilot and Tokenization Initiative
Uganda has commenced a central bank digital currency (CBDC) pilot, deploying a digitized version of the Ugandan shilling on Global Settlement Network’s (GSN) permissioned blockchain. Reporting via Cointelegraph, the pilot was announced on Wednesday as part of a broader initiative to tokenize $5.5 billion of real-world assets across the nation. This effort is a collaboration between blockchain financial firm GSN and Ugandan developer Diacente Group, aimed at advancing the digital economy and infrastructure in Uganda.
According to the official announcement, the new CBDC is backed by Ugandan treasury bonds and can be accessed via smartphone. The project also observes strict compliance, following international and local Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) protocols.
Africa’s Crypto Landscape and Adoption Trends
Sub-Saharan Africa, which includes Uganda and Kenya, continues to show rapid growth in cryptocurrency adoption. A Chainalysis report highlights the region as the third-fastest growing globally, with $205 billion in onchain value received between July 2024 and June 2025. Tokenization efforts in Uganda will span key sectors such as agro-processing facilities, mining, and solar energy production, aiming to digitize physical infrastructure and financial flows.
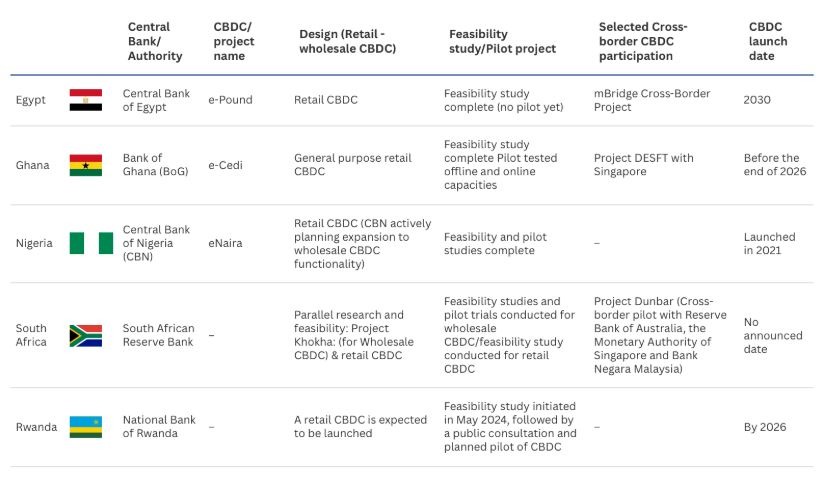
The CBDC pilot seeks to “unlock long-term value for our people and our region,” Diacente Group chairman Edgar Agaba stated, as cited by Cointelegraph. Nigeria remains the first African nation to launch a CBDC in 2021, while Ghana, South Africa, and Egypt (set for 2030) are at various stages of CBDC implementation.
Kenya Advances Toward Crypto Regulation
In neighboring Kenya, the Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASP) bill passed through parliament on Tuesday and awaits President William Ruto’s signature to become law. If enacted, this bill will regulate exchanges, brokers, wallet providers, and token issuers, with oversight duties divided between the Central Bank of Kenya and the Capital Markets Authority. Key provisions include licensing requirements, consumer protections, KYC/AML standards as per the Financial Action Task Force, and penalties for deceptive practices.
The bill, first introduced in January, aims to bring robust regulatory oversight to Kenya’s growing crypto ecosystem, which is among the continent’s most active according to regional transaction volumes.
Market Outlook and Next Steps
Africa’s digital asset landscape is forecasted to expand significantly. Data platform Statista estimates that over 75 million users will participate in the African crypto space by 2026, contributing to a projected revenue of $5.1 billion. Stablecoins represent 43% of transaction volume in Sub-Saharan Africa, with Nigeria, South Africa, Ghana, Kenya, and Zambia leading in activity—Uganda ranks seventh in the region.
As Uganda’s CBDC pilot rolls out and Kenya nears crypto regulatory enactment, both nations are positioning themselves at the forefront of Africa’s digital finance transformation. These moves could set standards for compliance and innovation across the continent.
For more on digital currencies and tokenization, visit Vizi’s cryptocurrency coverage.



















